[백준 11723번 JAVA] 집합 (비트마스킹)
by mini_min백준 문제

비트마스킹 문제
처음에 set 자료구조로 풀었는데, 시간 초과 오류가 나서 찾아보니 비트마스킹 유형의 문제였다.
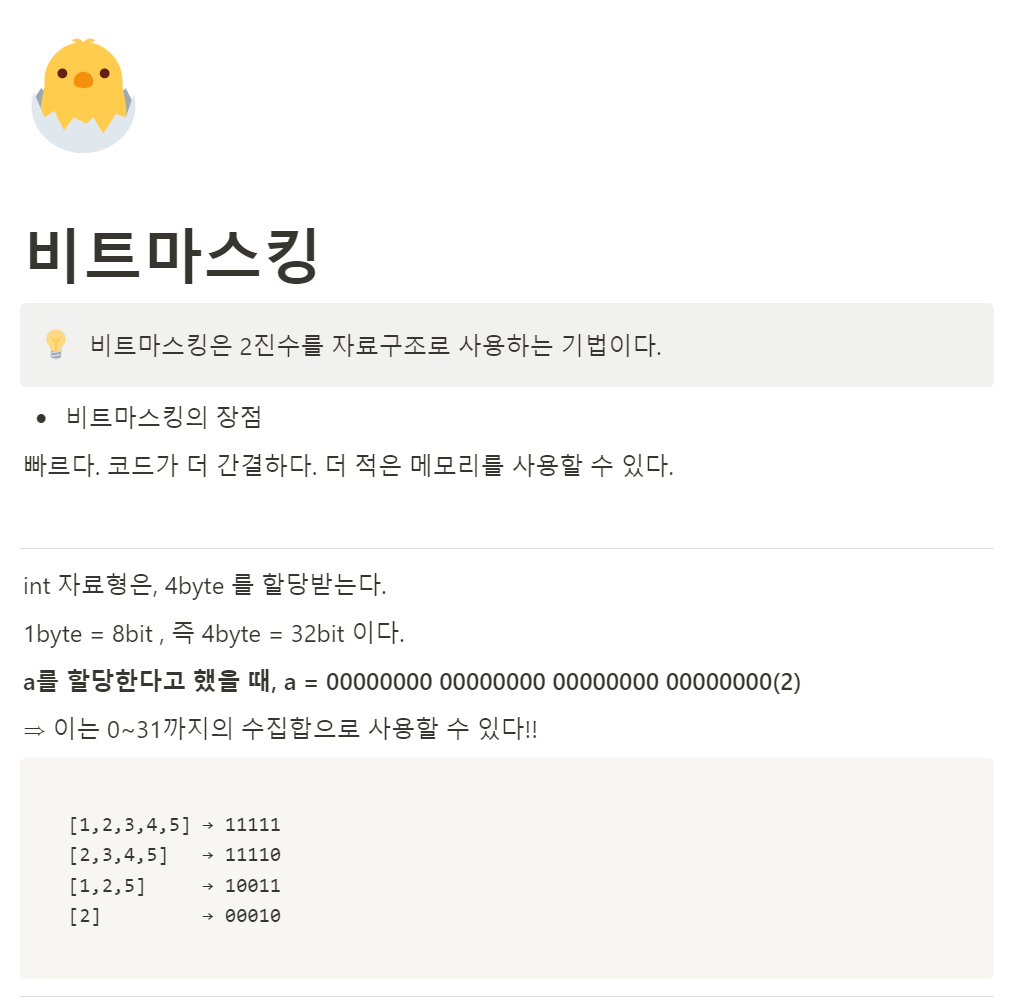
🪄 비트마스킹은 2진수를 자료구조로 사용하는 기법이다.
🎁 비트마스킹의 장점
빠르다. 코드가 더 간결하다. 더 적은 메모리를 사용할 수 있다.
int 자료형은, 4byte 를 할당받는다. 1byte = 8bit , 즉 4byte = 32bit 이다.
a를 할당한다고 했을 때, a = 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000(2)
⇒ 이를 활용해 0~31까지의 비트를 가지고 자료 구조로 사용할 수 있다!
[1,2,3,4,5] → 11111
[2,3,4,5] → 11110
[1,2,5] → 10011
[2] → 00010
숫자 num 이 주어졌을 때,
1. 삽입
a = a | 1 << num;
1. 삭제
a = a & ~(1 << num)
1. a 비우기
a = 0;
정답 코드
package baekjoon;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
//집합
//공집합 S 가 주어졌을 때, 아래 연산을 하는 프로그램을 작성하시오
/**
* add x : S에 x 추가 / S 에 이미 있는 경우 연산 무시
* remove x : x 제거 / x가 없는 경우 연산 무시
* check x : x가 있으면 1, 없는 경우 무시
* toggle : x가 있으면 x 제거, 없으면 x 추가
* all : S 를 { } 로 바꾼다.
* empty : S 를 공집합으로 변경
*/
public class _11723 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int num = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int arr = 0;
for ( int i = 0; i < num; i++ )
{
String[] target = br.readLine().split(" ");
int seat = 0;
if(! (target[0].equals("all") || target[0].equals("empty"))) {
seat = Integer.parseInt(target[1]);
}
switch (target[0])
{
case "add" : {
arr = arr | (1 << seat); //없는 경우 추가
break;
}
case "remove" : {
arr = arr & ~(1 << seat); //있는 경우 삭제
break;
}
case "all" : {
arr = (1 << 21) - 1; //다 채우기
break;
}
case "empty": {
arr = 0; //비우기
break;
}
case "toggle": {
arr = arr ^ (1 << seat);
break;
}
case "check": {
if( (arr & (1 << seat)) > 0) {
sb.append(1).append("\n");
} else {
sb.append(0).append("\n");
}
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
br.close();
}
}
'매일매일 알고리즘 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준 10431번 JAVA] 줄세우기 (Stack으로 어렵게 풀고 실패하기) (0) | 2024.04.10 |
|---|---|
| [백준 9655번 JAVA] 돌 게임 (1) | 2024.04.10 |
| [백준 23971번 JAVA] ZOAC 4 (0) | 2024.04.08 |
| [백준 JAVA] 11052번 풀이 - 카드 구매하기 (+16194번) (0) | 2023.11.23 |
| [백준 JAVA] 9095번 풀이 - 1, 2, 3 더하기 (DP) (0) | 2023.11.21 |
블로그의 정보
개발자 미니민의 개발로그
mini_min